Working with advanced rate limiting rules
Last updated 2023-06-14
Advanced rate limiting rules put a cap on how often an individual client can send requests that meet set conditions before all or some requests from that same client are blocked or logged.
Limitations and considerations
When working with advanced rate limiting rules, keep the following things in mind:
- Advanced rate limiting is only included with the Premier platform and certain packaged offerings. It is not included as part of the Professional or Essential platforms.
- Each site is limited to a maximum of 15 rate limit rules.
- A given signal can only be used as the threshold signal for a single rate limit rule. A signal can't be used as the threshold signal in more than one rate limit rule.
How advanced rate limiting rules work
When the web application you're protecting starts receiving requests that meet the conditions of a rate limit rule, the requests are tagged with the a user-selected signal called the threshold signal. Threshold signals are tallied and counted towards the threshold for that rule. When the threshold signal count for a single client exceeds the rule's threshold, that client is rate limited.
How the client is rate limited depends on the Match type and Action type fields for that rate limit rule. The Match type field defines which requests from the client should be blocked or logged after the threshold has been passed. Field options include:
- Rule conditions: rate limit requests from the client that match the rate limit rule's conditions. See an example use case of this option.
- Other signal: rate limit requests from the client that are tagged with a user-selected signal called the action signal. When the action signal is not an attack or anomaly signal, you need a request rule that tags requests with the selected signal. See an example use case of this option.
- All requests: rate limit all requests from the client.
The Action type field defines whether requests that meet the Match type condition should be blocked or logged. When the Action type field is set to Block, subsequent requests that meet the Match type are blocked and tagged with these signals:
- the threshold signal defined in the rule
Rate Limitsystem signalBlocked Requestsystem signal
When the Action type field is set to Log, subsequent requests that meet the Match type are logged and tagged with these signals:
- the threshold signal defined in the rule
Rate Limitsystem signal
Data storage
We store signal data based on the storage category of the signal.
| Signal | Signal type | Storage category |
|---|---|---|
| Threshold signal | Informational | Time series only |
Rate Limit | Anomaly | Sampled |
Blocked Request | Anomaly | Sampled |
Creating advanced rate limiting rules
To create an advanced rate limiting rule, start by navigating to the Add form for rules and selecting a type of rule:
- Log in to the Next-Gen WAF console.
- From the Sites menu, select a site if you have more than one site.
From the Rules menu, select Site Rules.
Click Add site rule.
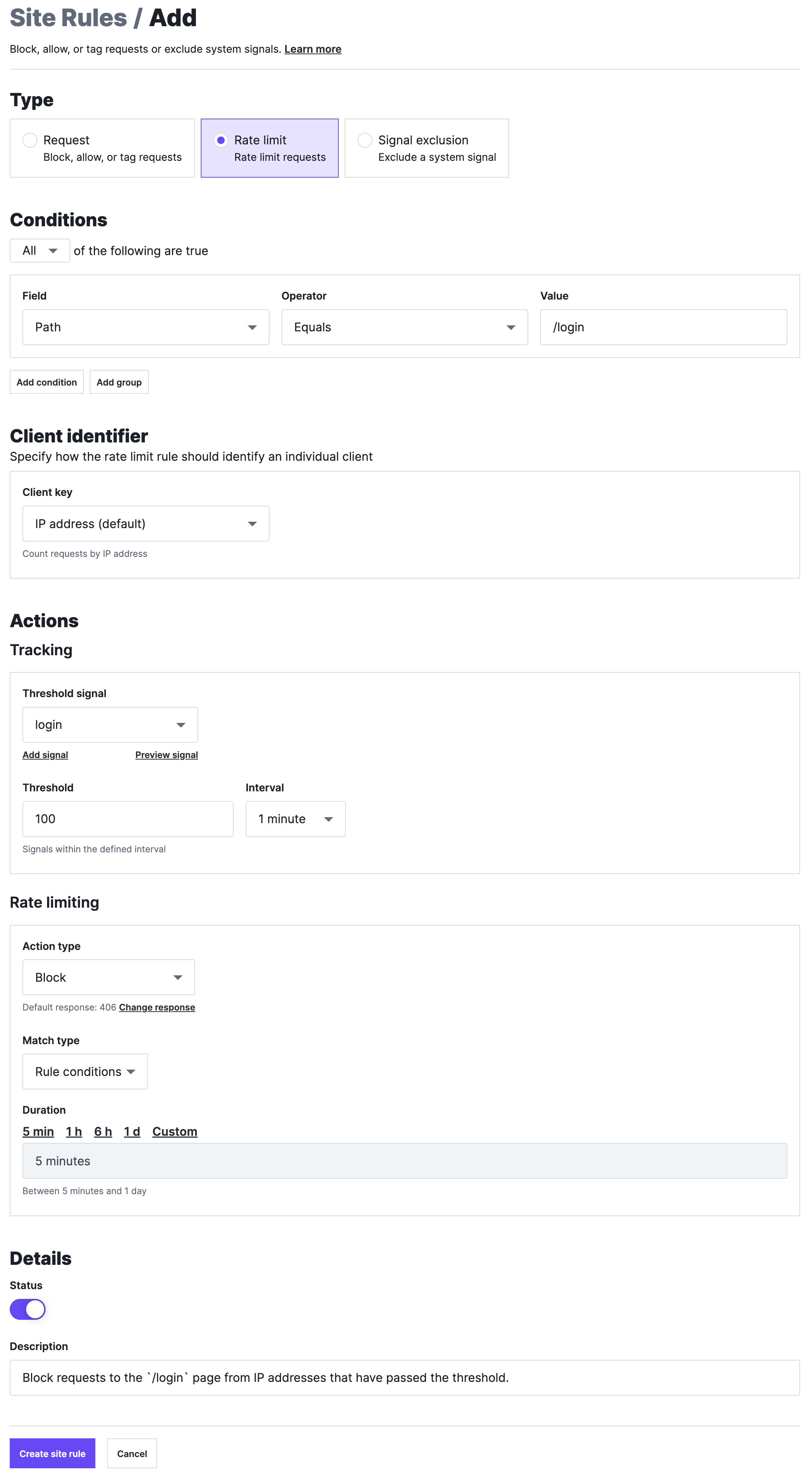
In the Type section, select Rate limit.
Next, define the logic that the rule should use to identify requests that count towards the threshold. In the Conditions section:
- Fill out these fields to create a condition:
- From the Field menu, select the request field that the condition is based on.
- From the Operator menu, select an operator to specify how the selected field and value relate.
- In the Value field, enter a value for the specified field.
- (Optional) Click Add condition to add another condition or Add group to create a group of conditions.
- Decide whether a request must meet one or all conditions in order to count towards the threshold:
- Select Any from the conditions menu to specify that a request must meet only one of the conditions you've created.
- Leave All selected in the conditions menu to specify that a request must meet every condition you've created.
Once you've done that, specify how the rate limit rule should identify an individual client. In the Client identifier section:
- From the Client key menu, select how the rate limit rule should identify a client. Depending on the Client key option you selected, additional client identifier fields may appear.
- (Optional) Fill out any additional fields that appeared in the Client identifier section.
Next, specify a signal that should be applied to requests that meet the rule's condition set and define the threshold. In the Actions section, fill out the Tracking subsection as follows:
- From the Threshold signal menu, select the signal that you want applied to requests that match the rule conditions. Requests tagged with the threshold signal are tallied and counted towards the threshold of the rule.
- In the Threshold field, enter the number of requests that must be detected before a client is rate limited.
- From the Interval menu, select the period of time requests must be detected during to pass the threshold.
Next, define how a client that exceeds the threshold should be rate limited. In the Actions section, fill out the Rate limiting subsection as follows:
- From the Action type menu, select the action that should be taken when the threshold has been exceed and requests meet the conditions of the match type. Action types include Block and Allow. When you select Block, the Change response link appears.
- (Optional) Click Change response to specify a custom response code to return when the rule blocks a request and fill out the related fields as follows:
- In the Response code (optional) field, enter a custom response code. Supported custom response codes are 301, 302, and 400-599.
- If you entered
301or302in the Response code (optional) field then, in the Redirect URL (optional) field, enter the absolute or relative URL of the redirect location. See Using redirect custom response codes.
- From the Match type menu, select the conditions that determine what should be rate limited once the threshold is exceeded. Options include:
- Rule conditions: rate limit requests from the client that match the rule's conditions. See an example use case of this option.
- Other signal: rate limit requests from the client that are tagged with the selected Action signal. When the action signal is not an attack or anomaly signal, you need a request rule that tags requests with the selected signal. See an example use case of this option.
- All requests: rate limit all requests from the client.
- From the Duration menu, select the amount of time the client should be rate limited.
Finally, add a description of the rule and save the rule:
- Fill out the Details section as follows:
- Leave the Status switch enabled.
- In the Description field, enter a description of the rule.
- Click Create site rule. The advanced rate limit rule is created, and the Site Rules page appears.
Example rate limit rules
The following examples demonstrate how to configure rate limit rules for common use-cases. Be aware that values (e.g., paths and response codes) used in these examples may not be the same as those used by your particular web application.
Rate limit comment submissions
This example rule demonstrates how to rate limit users' ability to submit comments:
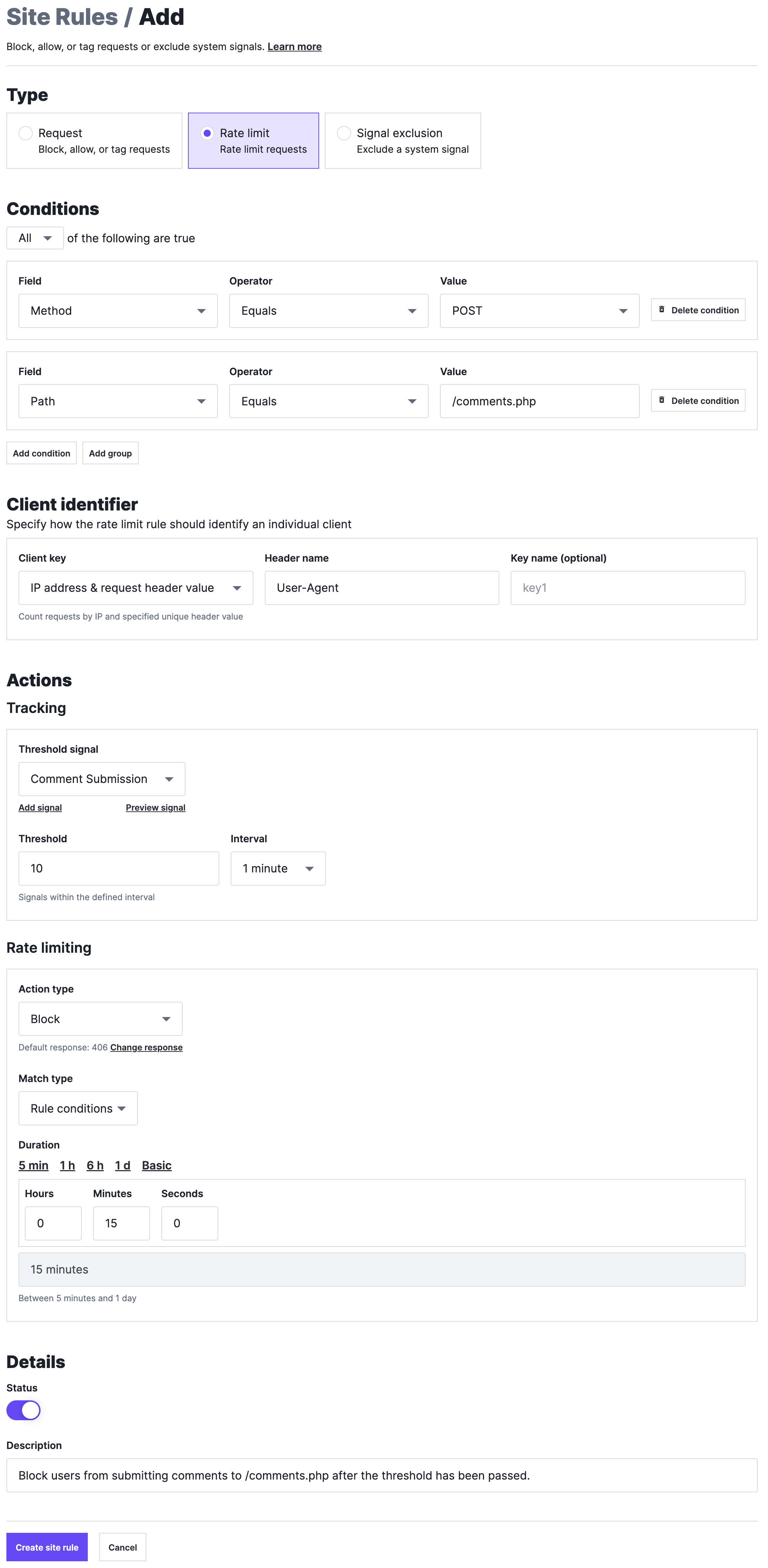
Specifically, the rule looks for POST requests to the /comments.php file and tags them with the Comment Submission custom signal (the Threshold signal). Because the user may attempt to change their IP address to circumvent the rate limit, the rule uses both the IP address and the value of the User-Agent request header (the Client identifier) to track requests from this user.
When 10 requests (the Threshold) tagged with the Comment Submission signal are detected from a unique IP address and User-Agent within 1 minute (the Interval), any subsequent requests with the Comment Submission signal from that IP address and User-Agent will be blocked (the Action type) for the next 15 minutes (the Duration).
Credit card validation attempts
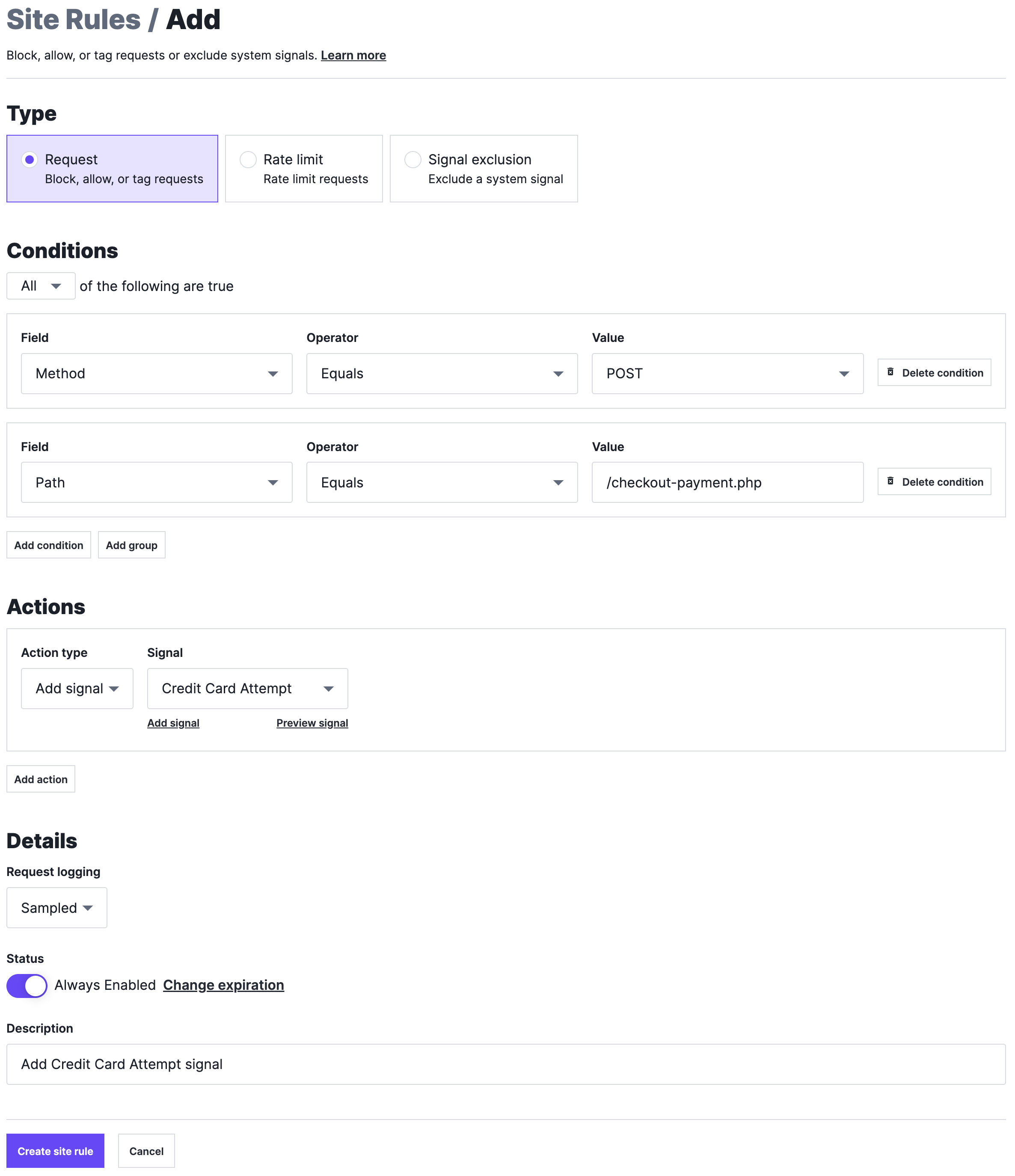
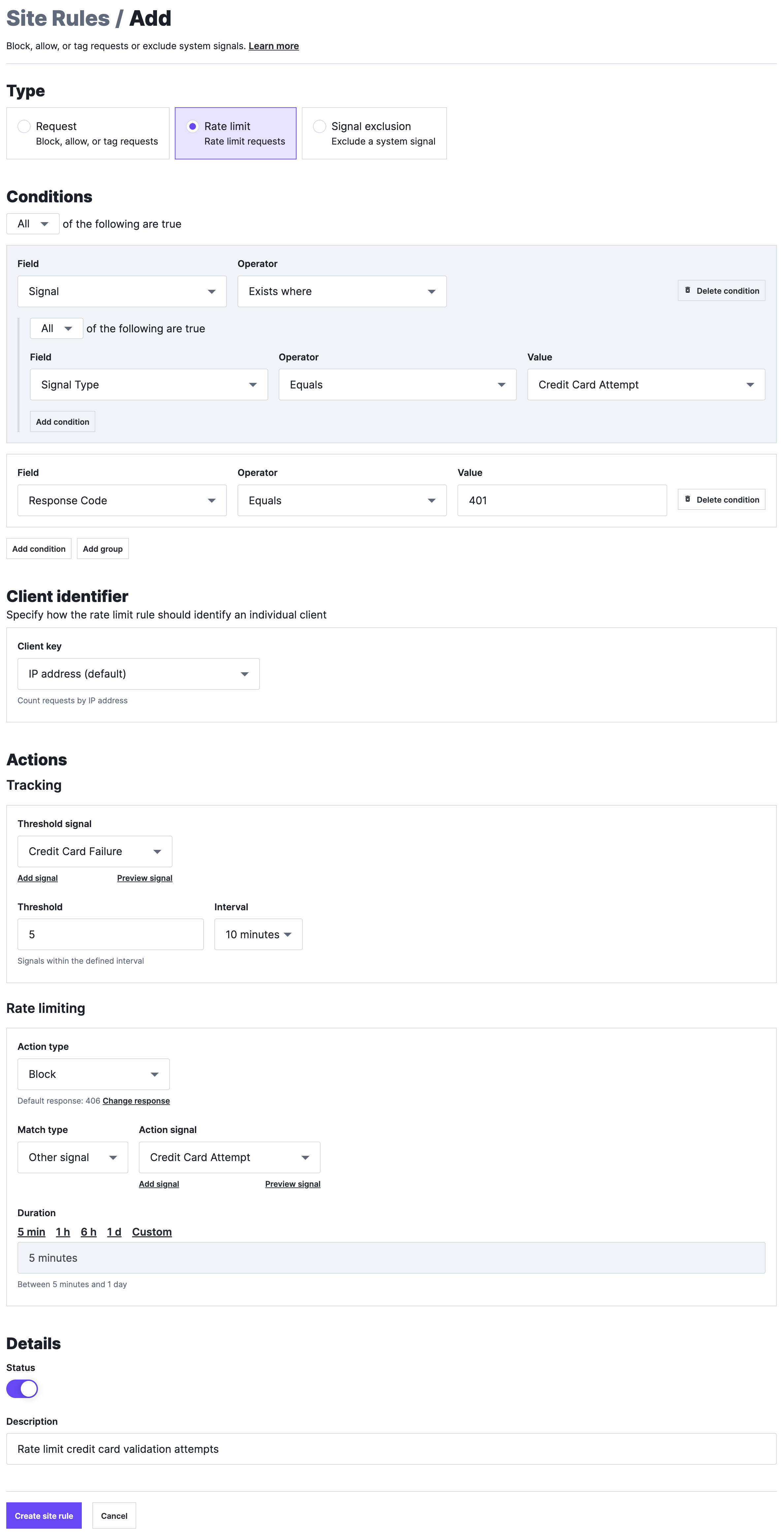
This example demonstrates how to rate limit credit card validation attempts after too many failed attempts. This use-case requires two separate rules:
- a request rule to track credit card validation attempts.
- a rate limit rule to track credit card validation failures and rate limit the originating IP address.
The request rule looks for POST requests to the /checkout-payment.php file and tags them with the Credit Card Attempt custom signal.
The rate limit rule looks for requests tagged with the Credit Card Attempt custom signal, as well as if the request received a 401 response code indicating the credit card validation attempt was a failure. The rule applies a Credit Card Failure custom signal (the Threshold signal) to these requests.
When 5 requests (the Threshold) tagged with the Credit Card Failure signal are detected from a signal IP within 10 minutes (the Interval), any subsequent requests tagged with the Credit Card Attempt signal (the Action signal) from that IP will be blocked (the Action type) for the next hour (the Duration).
Glossary
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Action type | Whether requests are logged or blocked. |
| Client | The source from where requests originate. |
| Client identifier | The parts of requests used to identify an individual client. |
| Duration | How long a client remains rate limited. |
| Interval | The period of time requests must be detected during to pass the threshold. |
| Match type | Which requests from the client should be blocked or logged after the threshold has been passed. |
| Threshold | How many requests must be detected before a client is rate limited. |
| Threshold signal | The signal that requests are tagged with when they meet the rate lime rule's condition set. Threshold signals are tallied and counted towards the threshold for that rule. When the threshold signal count for a single client exceeds the rule’s threshold, that client is rate limited. |
Do not use this form to send sensitive information. If you need assistance, contact support. This form is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.