Configuring Envoy proxy deployments
Last updated 2025-04-22
IMPORTANT
This guide only applies to Next-Gen WAF customers with access to the Next-Gen WAF control panel. If you have access to the Next-Gen WAF product in the Fastly control panel, you can only deploy the Next-Gen WAF with the Edge WAF deployment method.
Support is available for the Envoy Proxy via builtin Envoy gRPC APIs implemented in the sigsci-agent running as a gRPC server. Envoy v1.11.0 or later is recommended, however, Envoy v1.8.0 or later is supported with limited functionality as noted in the documentation below.
Envoy (as of v1.11) does not support a bidirectional gRPC API for inspecting traffic. There are instead two separate gRPC APIs available to inspect traffic. The External Authorization HTTP filter (envoy.filters.http.ext_authz) gRPC API allows the request to be held while waiting inbound request inspection, which allows for a request to be blocked if required. An additional gRPC AccessLog Service gRPC API can then be used to inspect the outbound request data. Using these two APIs together with the sigsci-agent running as a gRPC server allows for inspection in both directions using only Envoy builtin APIs. This allows web application inspection without installing a module for every upstream application. In this case the sigsci-agent is acting as the module.
Request allowed (normal) processing
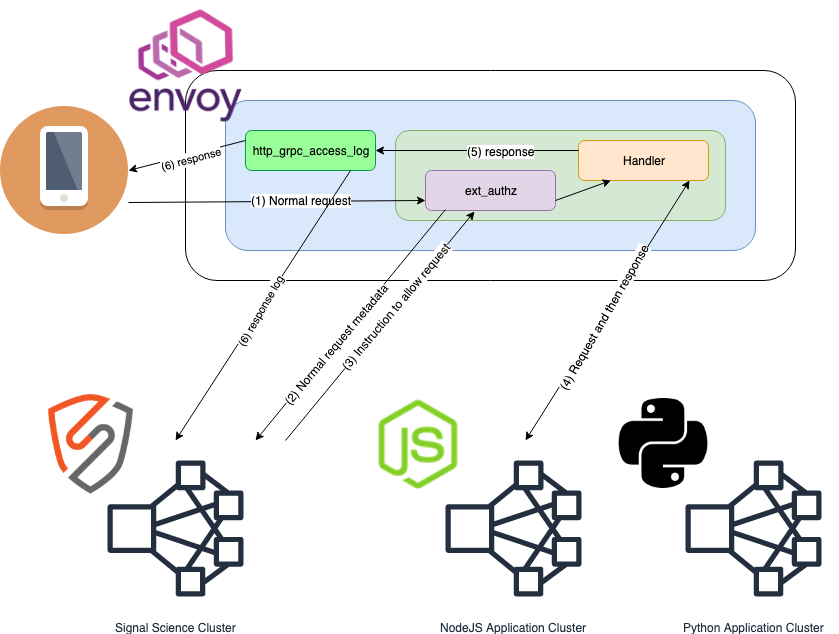
This is the flow for normal requests that the sigsci-agent allows through Envoy.
- Client request received by Envoy and routed to the Envoy
External Authorization (ext_authz)HTTP filter where request metadata is extracted for processing via thesigsci-agent. - Request metadata is sent to the
sigsci-agentvia gRPCext_authzAPI - The
sigsci-agentsends back an 'allow request' response allowing the request through theext_authzHTTP filter to continue normal Envoy request processing. - Request makes it through any additional HTTP filters to the Handler, which processes the request and generates the response.
- Request/Response metadata is extracted via the Envoy
gRPC AccessLog Service (als)asynchronously for processing via thesigsci-agent. - In parallel, additional metadata, such as response headers and the HTTP status code, is sent to the
sigsci-agentvia gRPCalsAPI for further processing while the response data is sent back to the originating client.
Request blocked processing
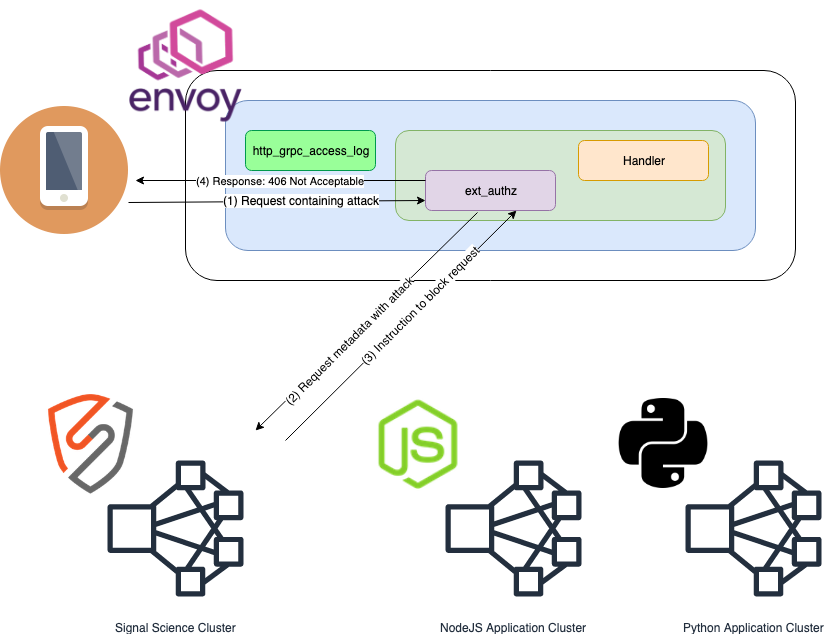
This is the flow if the sigsci-agent blocks a request from being processed through Envoy.
- Client request received by Envoy and routed to the Envoy
External Authorization (ext_authz)HTTP filter where request metadata is extracted for processing via thesigsci-agent. - Request metadata is sent to the
sigsci-agentvia gRPCext_authzAPI - The
sigsci-agentsends back a 'block request' response, disallowing the request to continue being processed by the HTTP filter chain. - This triggers the
ext_authzfilter to generate a HTTP 406 response, blocking the request from any further processing.
Next-Gen WAF agent configuration
The sigsci-agent is normally installed as a sidecar via Kubernetes with a slightly different configuration than a normal install.
The sigsci-agent must be configured to run with an Envoy gRPC listener instead of the normal RPC listener. To do this, configure the Envoy gRPC listener via the envoy-grpc-address agent configuration option, which will then start instead of the default RPC listener.
Setting the configuration value in the sigsci-agent config file:
envoy-grpc-address = "0.0.0.0:8000"Or setting the configuration value in the sigsci-agent environment:
SIGSCI_ENVOY_GRPC_ADDRESS=0.0.0.0:8000Optionally, the sigsci-agent can be configured with TLS enabled. To do this, set the certificate and key files in the sigsci-agent configuration.
envoy-grpc-cert = "/path/to/cert.pem"envoy-grpc-key = "/path/to/key.pem"Or
SIGSCI_ENVOY_GRPC_CERT=/path/to/cert.pemSIGSCI_ENVOY_GRPC_KEY=/path/to/key.pemAdditionally, it is recommended to enable response data processing. To do this, the sigsci-agent must be configured to expect response data from Envoy by setting the envoy-expect-response-data agent configuration option. By default, response data is ignored in the sigsci-agent as this is an optional Envoy configuration option in order to better support older versions of Envoy. If you are running Envoy v1.10 or higher, then you should enable this option.
Setting the configuration value in the sigsci-agent config file:
envoy-expect-response-data = 1Or setting the configuration value in the sigsci-agent environment:
SIGSCI_ENVOY_EXPECT_RESPONSE_DATA=1Some aspects of inspection in the sigsci-agent can be configured but generally should be left as the default. Check out inspection-* agent configuration for more details.
Envoy configuration
Envoy must to be configured with an External Authorization HTTP filter (envoy.filters.http.ext_authz) before the main handler filter to process request data and (optionally, though recommended) a gRPC AccessLog Service to process response data. To do this, multiple configuration items must to be added to the Envoy configuration: a cluster to handle the gRPC calls via the sigsci-agent, the envoy.filters.http.ext_authz HTTP filter before the main handler, and the envoy.http_grpc_access_log service added to the access_log section of the HTTP listener filter if response data is to be enabled.
Adding the Next-Gen WAF agent cluster
A cluster must be added which is configured with the Envoy gRPC address used in the sigsci-agent configuration. Currently load balancing will not work correctly if response data is enabled as there is not a way to enable consistent hashing for gRPC services in Envoy (yet), so it is recommended not to configure load balancing at this time unless only the envoy.filters.http.ext_authz API is being used without response data inspection.
1234567891011121314151617clusters: - name: sigsci-agent-grpc connect_timeout: 0.2s type: strict_dns #lb_policy: LEAST_REQUEST http2_protocol_options: {} #tls_context: {} ### You can also use 'hosts' below, but this is deprecated load_assignment: cluster_name: sigsci-agent-grpc endpoints: - lb_endpoints: - endpoint: address: socket_address: address: sigsci-agent port_value: 8000The address is a resolvable hostname or IP for the sigsci-agent and the port_value must match that configured in the sigsci-agent configuration for the envoy-grpc-address option.
NOTE
The connect_timeout is the timeout to connect to the sigsci-agent (but not to process the data) and can be adjusted if required. The tls_context option must be defined if TLS is to be used. TLS can be configured in the sigsci-agent config via envoy-grpc-cert and envoy-grpc-key. If TLS is configured in the sigsci-agent, then just the empty tls_context must be configured (e.g., `tls_context: ) to let Envoy know to connect via TLS. If certificate validation is desired, then validationcontext must be configured in the tlscontext to specify a trustedca filename to use for validation. As gRPC services are HTTP/2 based, the http2protocol_options: option is required so that traffic is sent to the sigsci-agent` cluster as HTTP/2.
Adding the Envoy External Authorization HTTP filter
The listener must have an External Authorization HTTP filter (envoy.filters.http.ext_authz) added before the main handler which points at the sigsci-agent cluster.
123456789101112131415161718192021222324http_filters:- name: envoy.filters.http.ext_authz typed_config: "@type": type.googleapis.com/envoy.extensions.filters.http.ext_authz.v3.ExtAuthz transport_api_version: V3 grpc_service: envoy_grpc: cluster_name: sigsci-agent-grpc timeout: 0.2s failure_mode_allow: true with_request_body: # Maximum request body bytes buffered and sent to the sigsci-agent max_request_bytes: 8192 # NOTE: If allow_partial_message is set false, then any request over # the above max bytes will fail with an HTTP "413 Payload Too Large" # so it is recommended to set this to true. allow_partial_message: true # NOTE: By default, envoy carries the HTTP request body as a UTF-8 string # and it fills the body @ # field. To pack the request body as raw bytes, # set pack_as_bytes to true. pack_as_bytes: true- name: envoy.filters.http.router typed_config: "@type": type.googleapis.com/envoy.extensions.filters.http.router.v3.RouterNOTE
failure_mode_allow: true is so that this will fail open, which is recommended. And timeout allows failing with the defined failure mode (true for fail open, false for fail closed) after a given time duration. Once this is done, all HTTP requests will be first sent to the envoy.filters.http.ext_authz filter handled by the sigsci-agent cluster. The sigsci-agent will then process requests and deny auth with a 406 HTTP status code if the request is to be blocked or allow the request through to the next HTTP filter if it is allowed. Any additional HTTP request headers are also added to the request as they are in other modules.
Adding the Envoy gRPC AccessLog Service
NOTE
This is a recommended, but optional step. If it is configured in Envoy, then the agent must also be configured to expect response data by setting the envoy-expect-response-data agent configuration option as noted in the Next-Gen WAF agent configuration section. The Envoy External Authorization (envoy.filters.http.ext_authz) HTTP Filter can only process request data. As the sigsci-agent needs the response data for full functionality, a gRPC AccessLog Service must be set up to send the response data to the sigsci-agent. To do this an access_log section must be added to the Envoy configuration under the listener filter (typically under the envoy.filters.network.http_connection_manager filter) if it does not already exist. If it does exist, then it must be appended to.
Refer to the access_log configuration option of the HTTP Connection Manager for more details. An envoy.http_grpc_access_log entry must be added here (in addition to any other existing access log entries).
Recommended Configuration (see Limitations and considerations for further customizations to minimize limitations):
123456789101112131415161718192021222324access_log:- name: envoy.http_grpc_access_log typed_config: "@type": type.googleapis.com/envoy.extensions.access_loggers.grpc.v3.HttpGrpcAccessLogConfig common_config: log_name: "sigsci-agent-grpc" transport_api_version: V3 grpc_service: envoy_grpc: cluster_name: sigsci-agent-grpc timeout: 0.2s additional_request_headers_to_log: # These sigsci-agent headers are required for correct processing: - "x-sigsci-request-id" - "x-sigsci-waf-response" # Optionally, additional headers can be added that should be recorded: - "accept" - "content-type" - "content-length" additional_response_headers_to_log: - "date" - "server" - "content-type" - "content-length"Limitations and considerations
Here are the current limitations when using the sigsci-agent with Envoy Proxy. As support for Envoy Proxy improves in the future, these limitations will be addressed and should be reduced.
No request bodies are processed by default
Prior to Envoy v1.10.0, the Envoy External Authorization did not send the request body. In all versions of Envoy, the request body is not included in the ext_authz call by default and it will not be inspected by the sigsci-agent unless configured.
For Envoy v1.10.0 or higher, support to include the request body is built in to the envoy.filters.http.ext_authz configuration and it is now possible to configure the with_request_body in this section of the Envoy configuration as noted above.
For Envoy v1.11.0 or higher, support was extended to be able to detect partial bodies more accurately.
For HTTP/2 (and gRPC) support Envoy must be running a version later than v1.12.1.
In Envoy v1.10.0 - v1.12.1 Envoy is not properly sending the request body using with_request_body.
However, it is possible to work around this Envoy limitation using Lua until an Envoy upgrade is possible. The following is an example Lua filter that can be used to pass on gRPC based bodies to the sigsci-agent for inspection:
To do this, the Lua HTTP filter (envoy.lua) HTTP filter can be configured before the envoy.ext_authz filter to add an internal x-sigsci-encoded-body header with this data.
A small snippet of Lua code must be added to extract the body and add it to the request as follows:
1234567891011121314151617181920212223242526272829303132333435363738394041http_filters: - name: envoy.lua config: inline_code: | -- Add a special header to pass the encoded body function envoy_on_request(req) local len = 0 local reqbody -- Determine the body length local cl = req:headers():get("content-length") if cl ~= nil then len = tonumber(cl) end -- gRPC does not have a content-length header to limit the body before buffering if len == 0 and req:headers():get("content-type") == "application/grpc" then -- Triggers buffering len = req:body():length() end -- Limit body length sent to the agent (adjust as needed) if len > 0 and len <= 8192 then -- Triggers buffering reqbody = req:body():getBytes(0, len) -- Encode the body for use in a header value local enc, t = string.gsub(reqbody, "[^%w]", function(chr) return string.format("%%%02X",string.byte(chr)) end) req:headers():add("x-sigsci-encoded-body", enc) end end - name: envoy.ext_authz config: grpc_service: envoy_grpc: cluster_name: sigsci-agent-grpc timeout: 0.2s failure_mode_allow: true# with_request_body:# max_request_bytes: 8192# allow_partial_message: true - name: envoy.router config: {}No TLS handshake metadata is extracted
There is not currently a means for the sigsci-agent to see the TLS handshake metadata (e.g., cipher and protocol version) used in the originating request as this is not (yet) available in Envoy. Any TLS handshake metadata based signals will not be seen in the product for this site (also known as a workspace).
The following system signals are currently not supported due to this limitation:
- WEAKTLS
Only minimal request headers are recorded by default if there were only response-based signals
If the request was inspected by the envoy.filters.http.ext_authz filter and no signals were issued, then the response will be processed by the envoy.http_grpc_access_log service. If a signal is found in the response data, then only minimal request headers will be recorded with the signal due to the API not being sent all request headers by default. However, if additional request headers are desired to be recorded, then these should be added via the additional_request_headers_to_log option of the access_log configuration in Envoy.
Currently these headers will automatically be added:
HostUser-AgentRefererX-Forwarded-For
Two sigsci-agent specific headers must be added. Additionally any additional request headers can be added explicitly via additional_request_headers_to_log:
123456789additional_request_headers_to_log:# These sigsci-agent headers are required for correct processing:- "x-sigsci-request-id"- "x-sigsci-waf-response"# Optionally, additional headers can be added that should be recorded:- "accept"- "content-type"- "content-length"- "x-real-ip"No response headers are processed by default
Similar to above with minimal request headers not being processed by the envoy.http_grpc_access_log service, there are no response headers sent to this API by default. Any headers that are desired to be recorded must be explicitly listed in the additional_response_headers_to_log option of the access_log configuration in Envoy as there is not currently any means to wildcard this. The following are recommended.
12345additional_response_headers_to_log:- "date"- "server"- "content-type"- "content-length"Sample deployment
The Sample deployment configuration section contains a complete Envoy proxy deployment configuration, which you can use as a starting point for your own deployment. For the sample configuration to work, complete the following steps:
Update the agent keys for your site (also known as workspace) by running the following command:
$ kubectl create secret generic sigsci.<site-name> \--from-literal=accesskeyid=<access-key-id> \--from-literal=secretaccesskey=<secret-access-key>Be sure to replace
<site-name>with the name of your site (workspace) and<access-key-id>and<secret-access-key>with your agent keys.Save the Sample deployment configuration as
envoy-deployment.yaml.Deploy
envoy-deployment.yamlby running the following command:$ kubectl apply -f envoy-deployment.yaml(Optional) Set up port forwarding and test the deployment locally by running the following command:
$ kubectl port-forward svc/envoy 10000:10000
Sample deployment configuration
123456789101112131415161718192021222324252627282930313233343536373839404142434445464748495051525354555657585960616263646566676869707172737475767778798081828384858687888990919293949596979899100101102103104105106107108109110111112113114115116117118119120121122123124125126127128129130131132133134135136137138139140141142143144145146147148149150151152153154155156157158159160161162163164165166167168169170171172173174175176177178179180181182183184185186187188189190191192193194195196197198199# ConfigMap: Contains the Envoy configuration with ext_authz integration.apiVersion: v1kind: ConfigMapmetadata: name: envoy-configdata: envoy.yaml: | node: id: proxy-node cluster: proxy-cluster static_resources: listeners: - name: listener_0 address: socket_address: address: 0.0.0.0 port_value: 10000 filter_chains: - filters: - name: envoy.filters.network.http_connection_manager typed_config: "@type": type.googleapis.com/envoy.extensions.filters.network.http_connection_manager.v3.HttpConnectionManager stat_prefix: ingress_http route_config: name: local_route virtual_hosts: - name: backend domains: ["*"] routes: - match: prefix: "/" route: cluster: edge_cluster host_rewrite_literal: "http.edgecompute.app" cors: allow_origin_string_match: - prefix: "*" allow_methods: GET, PUT, DELETE, POST, OPTIONS allow_headers: keep-alive,user-agent,cache-control,content-type,content-transfer-encoding,custom-header-1,x-accept-content-transfer-encoding,x-accept-response-streaming,x-user-agent,x-grpc-web,grpc-timeout max_age: "1728000" expose_headers: custom-header-1,grpc-status,grpc-message
access_log: - name: envoy.access_loggers.stdout typed_config: "@type": type.googleapis.com/envoy.extensions.access_loggers.stream.v3.StdoutAccessLog - name: envoy.http_grpc_access_log typed_config: "@type": type.googleapis.com/envoy.extensions.access_loggers.grpc.v3.HttpGrpcAccessLogConfig common_config: log_name: "sigsci-agent-grpc" transport_api_version: V3 grpc_service: envoy_grpc: cluster_name: sigsci-agent-grpc timeout: 0.2s additional_request_headers_to_log: # These sigsci-agent headers are required for correct processing: - "x-sigsci-request-id" - "x-sigsci-waf-response" # Optionally, additional headers can be added that should be recorded: - "accept" - "content-type" - "content-length" additional_response_headers_to_log: - "date" - "server" - "content-type" - "content-length"
http_filters: # ext_authz filter calls the NGWAF agent via gRPC. - name: envoy.filters.http.ext_authz typed_config: "@type": type.googleapis.com/envoy.extensions.filters.http.ext_authz.v3.ExtAuthz transport_api_version: V3 grpc_service: envoy_grpc: cluster_name: sigsci-agent-grpc failure_mode_allow: false - name: envoy.filters.http.router typed_config: "@type": type.googleapis.com/envoy.extensions.filters.http.router.v3.Router clusters: # Cluster for forwarding requests to https://http.edgecompute.app. - name: edge_cluster connect_timeout: 0.25s type: LOGICAL_DNS lb_policy: ROUND_ROBIN load_assignment: cluster_name: edge_cluster endpoints: - lb_endpoints: - endpoint: address: socket_address: address: http.edgecompute.app port_value: 443 transport_socket: name: envoy.transport_sockets.tls typed_config: "@type": type.googleapis.com/envoy.extensions.transport_sockets.tls.v3.UpstreamTlsContext sni: "http.edgecompute.app" # Cluster used by the ext_authz filter to contact the NGWAF agent. - name: sigsci-agent-grpc connect_timeout: 0.25s type: STATIC lb_policy: ROUND_ROBIN http2_protocol_options: {} # <--- This tells Envoy to use HTTP/2 for gRPC load_assignment: cluster_name: sigsci-agent-grpc endpoints: - lb_endpoints: - endpoint: address: socket_address: # Both containers share the same network namespace. address: 127.0.0.1 port_value: 9999
---
# Deployment: Combines the Envoy proxy and the Next‑Gen WAF Agent sidecar.apiVersion: apps/v1kind: Deploymentmetadata: name: envoy-waf-deploymentspec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: app: envoy-waf template: metadata: labels: app: envoy-waf spec: containers: # Envoy container – set to use debug logging for detailed output. - name: envoy image: envoyproxy/envoy:v1.22-latest args: - "-c" - "/etc/envoy/envoy.yaml" - "-l" - "debug" # Change to "trace" for even more verbosity. ports: - containerPort: 10000 volumeMounts: - name: envoy-config mountPath: /etc/envoy # Next‑Gen WAF Agent container (sigsci-agent) configured for ext_authz (gRPC mode). - name: sigsci-agent image: signalsciences/sigsci-agent:latest imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent env: - name: SIGSCI_ACCESSKEYID valueFrom: secretKeyRef: name: sigsci.my-site-name-here key: accesskeyid - name: SIGSCI_SECRETACCESSKEY valueFrom: secretKeyRef: name: sigsci.my-site-name-here key: secretaccesskey # Instruct the agent to expect response data and configure its gRPC address. - name: SIGSCI_ENVOY_EXPECT_RESPONSE_DATA value: "1" - name: SIGSCI_ENVOY_GRPC_ADDRESS value: "localhost:9999" - name: SIGSCI_DEBUG_ALL_THE_THINGS value: "true" - name: SIGSCI_WAF_DATA_LOG value: "/dev/stdout" ports: - containerPort: 9999 securityContext: readOnlyRootFilesystem: true volumes: - name: envoy-config configMap: name: envoy-config
---
# Service: Exposes the Envoy listener on port 10000.apiVersion: v1kind: Servicemetadata: name: envoyspec: selector: app: envoy-waf ports: - protocol: TCP port: 10000 targetPort: 10000Next steps
Verify the agent and module installation and explore module options.
Do not use this form to send sensitive information. If you need assistance, contact support. This form is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.