- English
- 日本語
Enabling cross-origin resource sharing (CORS)
Last updated 2023-07-25
Enabling Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) allows a server to indicate that other origins can request sub-resources, like scripts and stylesheets, from it. These origins might use a different scheme (HTTP vs HTTPS) or an entirely different domain or port. This guide describes how to add an Access-Control-Allow-Origin header, which is sufficient for simple scenarios, and is often useful when using static bucket providers like Amazon S3 and Google Cloud Storage as an origin.
IMPORTANT
We recommend only enabling CORS when you have sub-resources on your server that you want other origins to load, especially if you allow requesting code from any origin, as it makes things less secure.
To enable CORS, set up a custom HTTP header for your service by following the steps below.
- Log in to the Fastly control panel.
- From the Home page, select the appropriate service. You can use the search box to search by ID, name, or domain.
- Click Edit configuration and then select the option to clone the active version.
- Click Content.
Click Create header.
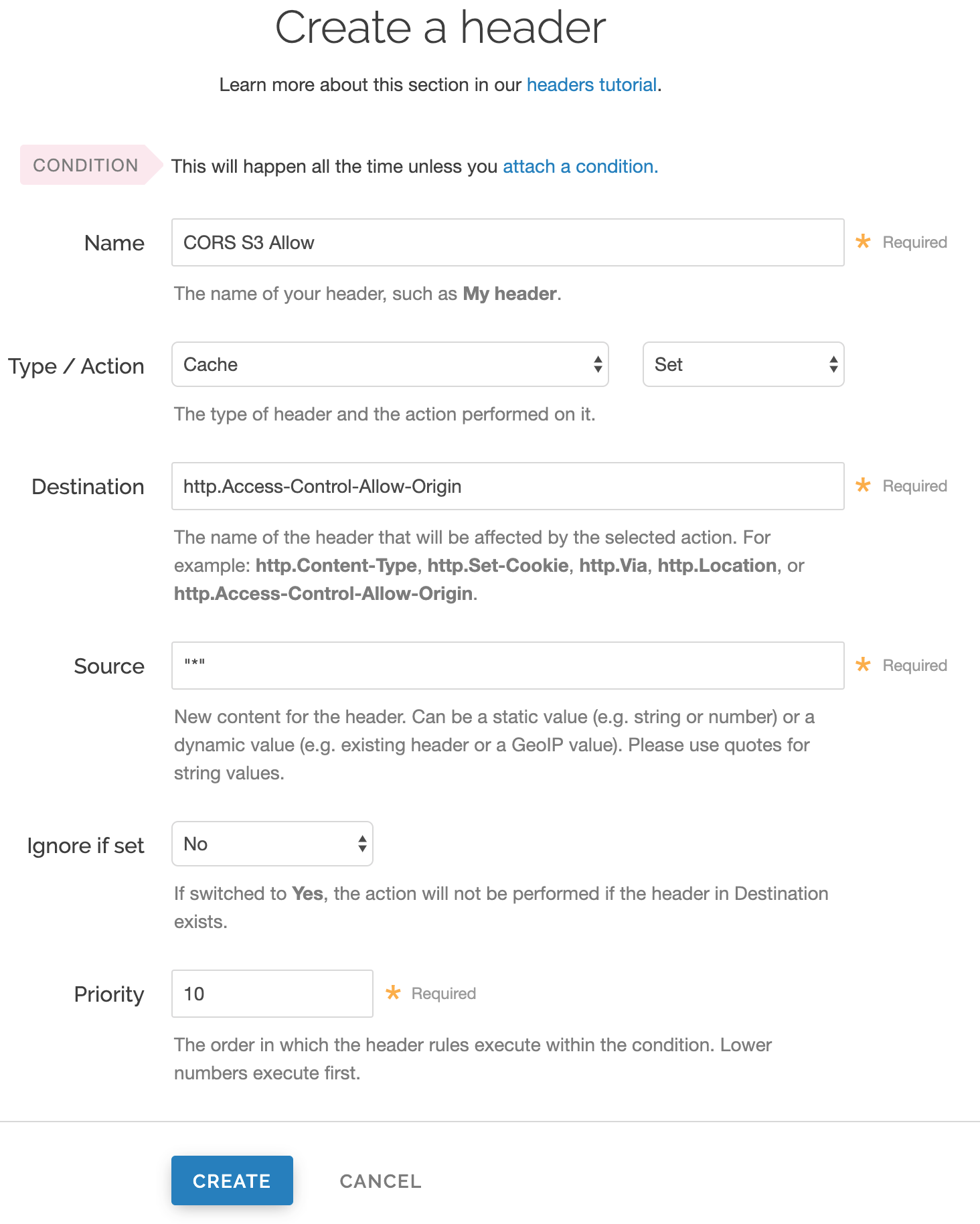
Do the following with the Create a header controls depending on whether you're creating a header for all origins or creating a header for a specific origin:
For this control When creating a header for any origin When creating a header for a specific origin Name Enter a descriptive name for the new header (e.g., CORS S3 Allow).Enter a descriptive name for the new header (e.g., CORS S3 Allow).Type Select Cache. Select Response Action Select Set. Select Set. Destination Enter http.Access-Control-Allow-Origin.Enter http.Access-Control-Allow-Origin.Source Enter "*".Enter a specific origin (e.g., https://example.com).Ignore if set Leave the default value. Leave the default value. Priority Leave the default value. Leave the default value. Any time you specify a single origin in the Source field to ensure CORS rules are applied in
vcl_deliver, the system will generate VCL undervcl_deliverasset resp.http.Access-Control-Allow-Origin = "<specified origin>";.Click Create. The new header appears on the Content page.
- Click Activate to deploy your configuration changes.
IMPORTANT
Objects already cached won't have this header applied until you purge them.
Test it out
Running the command:
$ curl -I example.tld/path/to/resourceshould include similar information to the following in your header:
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: http://example.tldAccess-Control-Allow-Methods: GETAccess-Control-Expose-Headers: Content-Length, Connection, Date...TIP
Access-Control-Allow-Methods and Access-Control-Expose-Headers are examples of additional headers you can add with CORS. For more information about these headers, check out MDN Web Docs.
Do not use this form to send sensitive information. If you need assistance, contact support. This form is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.